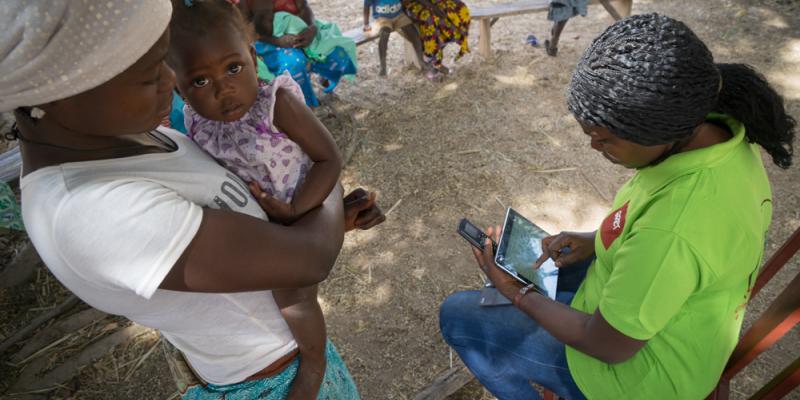
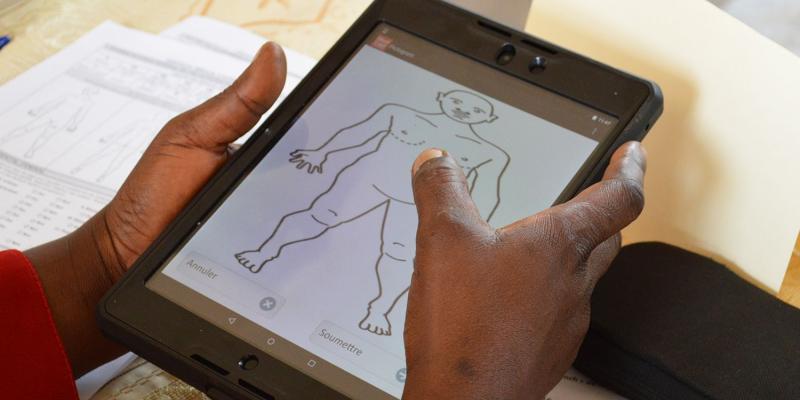
Zanzibar faces high levels of neonatal mortality as a result of delays or inability to seek care and biological risk factors that go undetected due to lack of contact with providers. Moreover, the health system in general suffers from a lack of resources, especially for Community Health Workers (CHWs).
The Government of Zanzibar is implementing a national digitally-supported community health program to provide essential health, nutrition, and development services to pregnant women and children.
In that framework, machine learning (ML) is an innovative approach that has potential to improve effectiveness and efficiency of service delivery of Maternal Neonatal and Child Health (MNCH).
The project aimed to personalize and improve MNCH in Zanzibar by integrating predictive analytics into the national digital community health system using machine learning. This innovation has tried enable CHWs to pre-identify women with high-risk pregnancies and target prenatal and postnatal services to mitigate risk and improve outcomes.
The solution builded on a highly effective digital system that has been implemented since 2011 in partnership with the Ministry of Health (MOH) in Zanzibar. The system gave the project unique access to comprehensive longitudinal client data that is continuously updated.
- 93% of women that were identified as high-risk received at least one additional CHV visit = 3182 out of 3422
- All CHVs (194) and supervisors (19) involved in the pilot project were trained on the use of the app in the two concerned districts in Zanzibar